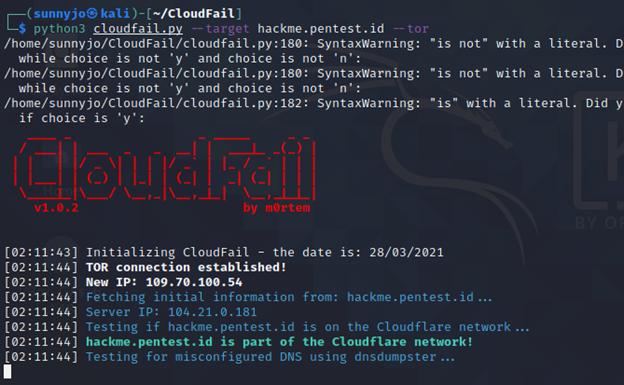
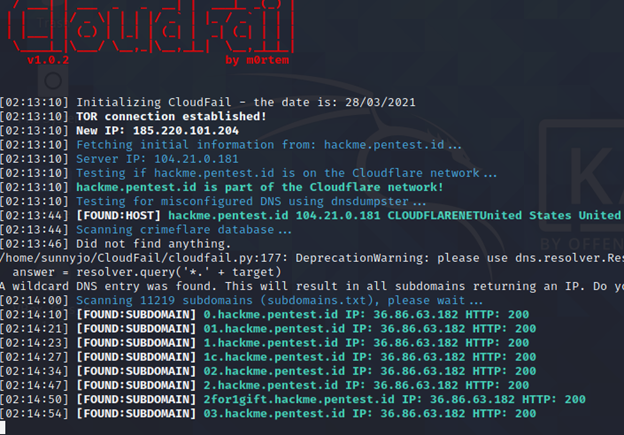
Sunny Jovita – 2031939046
Week 13
Disclaimer: This blog is for educational purposes only.
Ubuntu is a Linux based Operating System and belongs to Debian family of Linux. Since it is Linux based, it is freely available for use and it’s open source.
Kali Linux is an open source open source operating system and it is freely available for use. Kali Linux comes packed with 100+ of penetration testing, security research, digital forensics, reverse engineering, and ethical hacking tools.
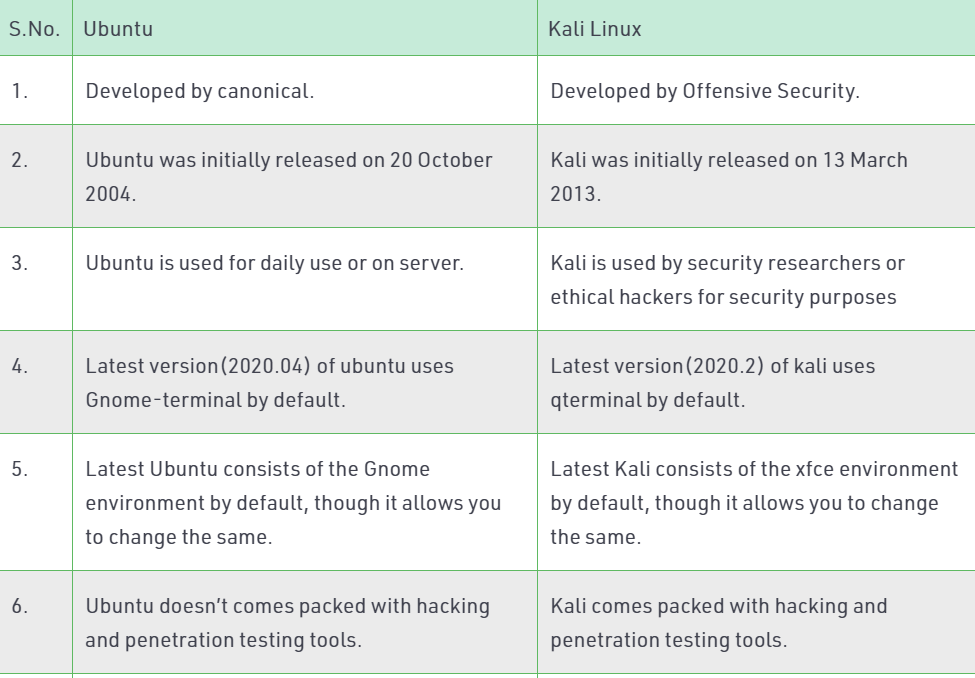
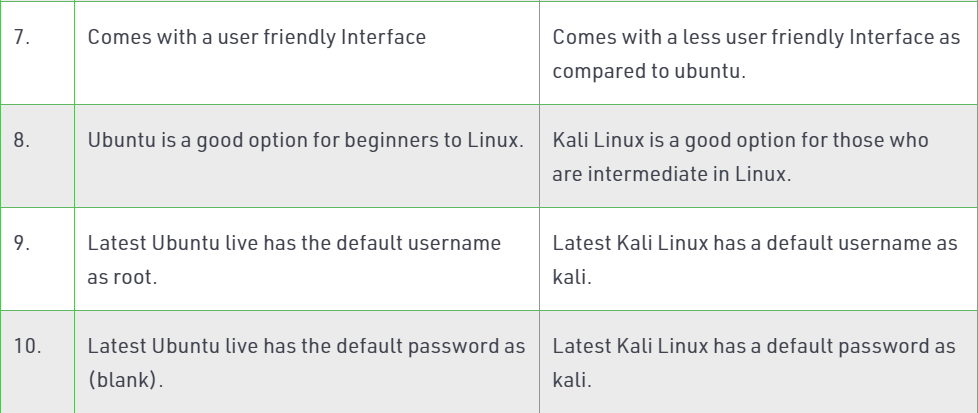
However, apart from the differences above, it is not fair to compare them on the same level. In my opinion, if you are looking for operating system for network security, penetration testing, etc, Kali Linux is the best choice. Nevertheless, if you want a user friendly, general purpose operating system with the best GUI, Kali Linux cannot compete Ubuntu.
In other words, we can describe Ubuntu and Kali Linux below:
- Ubuntu is more suited for personal uses and beginners who want to learn Linux. It is also used by many people who want their computer to be virus safe. I other words Ubuntu is user friendly general desktop/laptop operating system.
- Meanwhile, Kali Linux was Backtrack and Backtrack was Ubuntu with penetration packages installed. Kali comes with a number of penetration tools be it wifi or databases, build to be used instantly.